
by Joy Maitland | Aug 12, 2025 | All Employees, Board Members, Board Trustees, CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, Emerging Leaders, General Managers, Heads of Divisions, Human Resources (HR), News & Articles
Balancing Excellence with Sustainability
(Because “high performance” should not mean “high casualties”)
Here is the paradox no one in the boardroom wants to talk about:
Your relentless push for excellence might be the very thing eroding it.
We glorify high standards. We applaud the extra mile. We celebrate the hero who answers emails at 1:00 a.m. But excellence without sustainability is like running a Formula 1 car at top speed without ever changing the tyres — it looks impressive until it does not finish the race.
What the data says
McKinsey’s “Performance through People” research shows that the top-performing companies (“P + P Winners”) do not just demand results — they design systems where employee autonomy, clear challenge from leaders, and inclusive, supportive workplaces all coexist. This combination outperforms high-pressure, low-support environments on both revenue growth and retention.
Goldman Sachs offers an old-school example with a modern twist: their apprenticeship model couples intense performance expectations with coaching, mentoring, and long-term talent development. That mix keeps people sharp and standing.
The uncomfortable truth:
Many leaders think they are building excellence when, in fact, they are building exhaustion. Burnout is not a badge of honour — it is a business risk. The World Health Organization recognises burnout as an occupational phenomenon because it directly undermines performance, creativity, and health.
Three ways to rewrite the playbook:
- Bake recovery into delivery – Treat downtime as part of the performance cycle, not a guilty pleasure.
- Prioritise in public – Share openly what will not be done this quarter so teams know you mean it when you say “focus.”
- Share ownership of excellence – Stop making quality the responsibility of a handful of perfectionists. Train every team member to own standards — and make it safe to flag when those standards are at risk.
Why this matters more than you think
A culture that matches high standards with pacing, wellbeing, and scenario planning sends a signal: We win the long game. And that is where true competitive advantage lives.
The question to wrestle with: If your team sustained your current pace for the next 24 months, would you still have the same people — and the same quality — at the end of it? If you hesitate, your “excellence” might already be unsustainable.
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.

by Atiya Sheikh | Aug 12, 2025 | All Employees, Board Members, CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, General Managers
Building Trust Through Transparent Systems
(Why leaders who “show their workings” win more than just respect)
Here is a question for you: if your organisation’s performance review process was leaked to the press tomorrow, would you be proud—or scrambling to rewrite it?
That is not a hypothetical to make you sweat. It is a reality check. Because the truth is, trust is not built on charisma or charm. Trust is built in the small print—those unglamorous systems that dictate how people are evaluated, rewarded, and promoted.
Transparency is not about telling people everything.
It is about ensuring the “how” is as visible as the “what.” McKinsey’s data is uncomfortably clear: organisations that put people—not paperwork—at the centre of performance management are 4.2 times more likely to outperform their peers, 30% more likely to grow revenue, and see 5% lower attrition. (McKinsey link)
Gallup piles on another uncomfortable truth: employees who receive daily feedback are 2.1 times more likely to trust leadership, and if they believe their leaders genuinely listen, that trust more than doubles. (Gallup link)
Here is the twist:
Transparency is not a “feel-good” exercise. It is a strategic weapon. When you make your systems visible—warts and all—you remove the shadows where suspicion thrives. And when suspicion dies, collaboration flourishes.
If you are serious about this, try these experiments:
- Show the algorithm – Publish the exact performance review criteria. Let your team see how the sausage is made.
- Reverse-engineer decisions – For your next big call, publish the rationale. Every assumption. Every discarded option.
- Test the blindfold – Imagine handing your salary banding guidelines to someone in another department who has never met the individuals in question. If the process is truly clear and objective—based solely on role requirements, market benchmarks, and documented criteria—they should be able to determine the exact same pay range you would. If they cannot, it means your system is open to personal bias and inconsistent application.
- Make “why” a habit – Not just “what we decided,” but “why we decided it.” Every time.
The easy excuse is, “But people will not understand the complexity.” I would argue: if your people cannot understand your systems, that is your system’s fault—not theirs.
Transparency does not make you predictable. It makes you dependable. And in a world where the average worker trusts their employer more than government, media, or NGOs (Edelman Trust Barometer), dependability is the currency of leadership longevity.
So, one final challenge: what would your team say if they saw the inner workings today? If the answer is “they would leave,” you already have your real problem.
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.
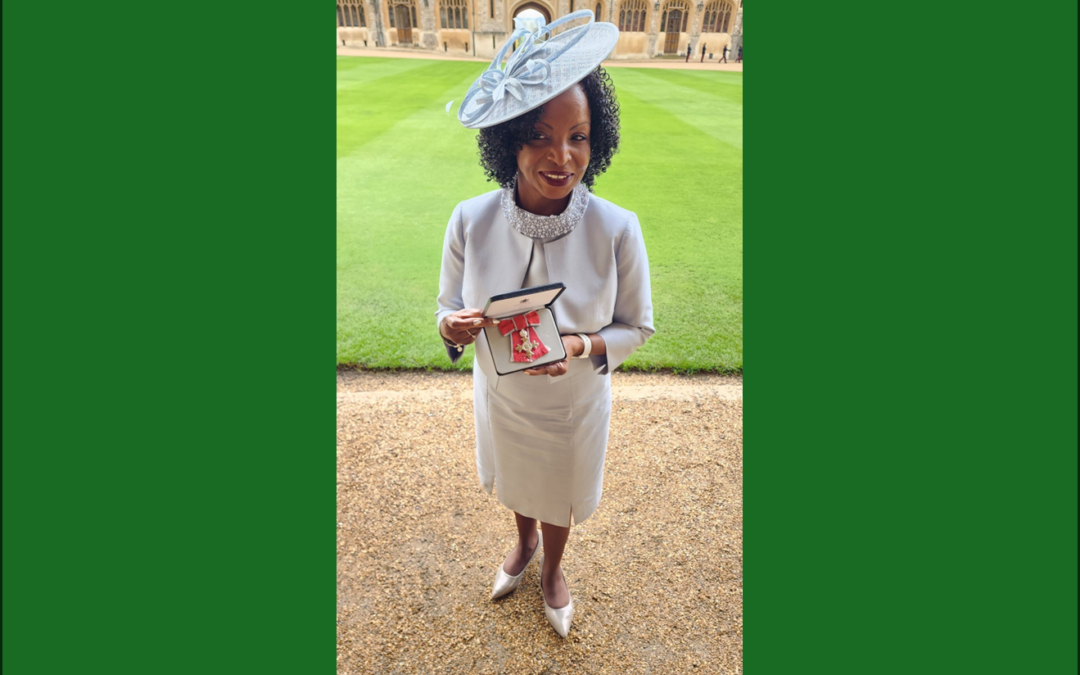

by Joy Maitland | Jul 1, 2025 | Awards
We celebrate Joy Maitland’s remarkable achievements and her recognition as a Member of the Order of the British Empire (MBE) in the King’s Birthday Honours 2024. She received this honour for her outstanding services to business and charity. This accolade reflects Joy’s commitment to making a positive impact, embodying her motto: ‘Be the difference that makes the difference.’
Career and Leadership Development
Joy’s career is a tapestry of dedication to personal and professional development. Her journey began in senior leadership roles where she recognised the untapped potential of junior staff, creating leadership development programmes that have since become a hallmark of her approach. Joy’s natural empathy and ability to connect with others have been instrumental in nurturing talent and encouraging growth.
Transformative Programmes and Initiatives
During her time as Board Member and Head of Leadership Development at the Amos Bursary, Joy created a transformative four-and-a-half-year programme that empowered young people of African and Caribbean heritage. Her initiatives, including launching the ‘Beyond Outstanding’ summer programme with Imperial College London and organising international work placements in New York, broke barriers and built confidence. Joy’s key role in the Bursary’s success earned her the title “keeper of the brand” from founder Colleen Amos.
Influence Across Organisations
Joy’s influence extends to numerous organisations. As Vice Chair of the Ekaya Housing Association, she worked with staff and other board members to champion affordable housing and community development. Her contributions to the Institute of Leadership, where she became the first black trustee in its 70-year history, and currently as Vice Chair at Plane Saver Credit Union—a leading financial cooperative —underscore her commitment to financial wellbeing and ethical practices. By assisting Code Your Future in launching their mentoring programme and supporting the leadership team as a volunteer, Joy is proud to have contributed to the charity’s mission of transforming lives through technology education.
Inemmo’s Impact
One of Joy’s proudest contributions is the Diploma Programme her company, inemmo, runs on behalf of the Cayman Islands government. This initiative aims to empower citizens to rise to the top of government and industry, reflecting Joy’s belief in the importance of nurturing local talent and leadership.
The multi-award-winning Inemmo, established by Joy in 2005 and an acronym for INspire, EMpower, and MOtivate, aims to be a catalyst for transformative leadership. The company is dedicated to empowering leaders with the skills, mindset, and courage to drive meaningful change and create a lasting impact. Since 2016, Inemmo has partnered with Lumina Learning to bring progressive professional employee recruitment and development tools to businesses in East and West Africa, significantly enhancing their talent acquisition and growth strategies.
Author and Advocate
In addition to her practical contributions to leadership, Joy is also an accomplished author. Her book, From Alpha to Zen: Leadership for a Brave New World, offers insightful guidance on cultivating effective leadership qualities. It provides readers with a roadmap to develop the skills and mindset necessary for driving meaningful change and creating a lasting impact in today’s dynamic business environment.
Commitment to Diversity and Inclusion
Diversity and inclusion are cornerstones of Joy’s philosophy. She tirelessly advocates for equitable representation, knowing that true creativity and innovation stem from diverse perspectives. Yet, she acknowledges the significant work still needed to achieve this vision, particularly in addressing systemic racism and ensuring minority representation in leadership.
Focus on Startups and Young Leaders
While Inemmo collaborates with many notable companies, it is the work with startups and young leaders that particularly motivates Joy. She is honoured and proud of these efforts, knowing they ensure not only growth but sustainability. Joy coaches leaders to ride the waves of adversity, build resilience, and take time to appreciate and celebrate their own unique gifts.
A Collective Honour
Joy’s receipt of an MBE is not just an individual honour but a collective celebration of all those she has inspired and uplifted. It is a call to continue her mission of cultivating self-aware, collaborative leadership and creating environments where everyone can thrive.
Legacy of Empowerment
Joy Maitland’s legacy is one of empowerment, resilience, and unwavering service to others. Her work, both in the UK and internationally, and through powerful initiatives like her virtual ‘Leading in Lockdown’ seminars during the pandemic, exemplifies her boundless dedication.
We congratulate Joy Maitland MBE on this well-deserved honour and look forward to her continued contributions to making the world a better place. Joy, your passion and perseverance inspire us all to ‘Be the difference that makes the difference.’

by Joy Maitland | May 25, 2025 | Board Members, Board Trustees, CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, General Managers, Heads of Divisions
Why Leaders Deny Facts — And What to Do About It
The Psychology Behind Strategic Blind Spots in Senior Decision-Making
In boardrooms, strategy sessions, and executive off-sites, a familiar pattern often emerges. Leaders ask for data, assess options, and demand analysis. Yet when the facts challenge deeply held assumptions or preferred outcomes, something subtle—but powerful—can happen.
– The facts get side-lined.
– The challenge gets dismissed.
– The truth gets buried.
This is not about ignorance or bad intentions. In fact, the most seasoned professionals—those with reputations to protect and legacies to defend—are often the most susceptible to motivated reasoning. This psychological tendency leads people to unconsciously filter information in ways that protect their identity, beliefs, or past decisions.
Understanding why this happens is not just an academic exercise. It’s a leadership imperative for anyone navigating disruption, innovation, or high-stakes decisions.
What Psychology Reveals: Three Experiments Every Leader Should Know
1. Motivated Reasoning in High-Stakes Environments
Research consistently shows that people are more likely to accept information that supports what they already believe—and to reject or scrutinise data that contradicts it. This pattern intensifies when:
-
Professional reputation is on the line
-
The decision is politically sensitive or emotionally loaded
-
The new information threatens an existing narrative
In one study, participants received balanced evidence on a controversial issue. Their conclusions differed dramatically—not because of the data, but because of what they already believed.
Leadership takeaway: Even in data-driven cultures, bias can masquerade as alignment. Leaders must question whether their objectivity is as robust as it appears.
2. The Backfire Effect: When Facts Reinforce False Beliefs
Another study attempted to correct factual misconceptions with evidence-based briefings. Surprisingly, those with higher education levels didn’t change their minds—they became even more entrenched in their original views.
This is known as the backfire effect: when facts not only fail to persuade but reinforce the falsehoods they aim to correct.
Leadership takeaway: Better data doesn’t always lead to better decisions. The urge to be “right” often outweighs the willingness to rethink.
3. The “Pay-to-Avoid” Experiment
Perhaps the most revealing experiment asked participants whether they’d prefer to read an article with an opposing viewpoint—or pay a small fee to avoid it. Many chose to pay, even when the article was balanced and respectful.
Leadership takeaway: If people avoid intellectual discomfort in a lab setting, imagine the avoidance behaviours that might surface in the boardroom—where hierarchy, politics, and performance pressures come into play.
Where Fact-Denial Shows Up in the C-Suite
When leaders ignore inconvenient truths, the ripple effects extend beyond individual decisions—they shape organisational culture. Here’s how fact-denial manifests at the senior level:
- Confirmation bias in forecasting: favouring data that supports preferred projections
- Groupthink in innovation: rejecting bold or unconventional ideas prematurely
- Suppressed challenge: excluding diverse or junior voices from decision-making
- Narrative inertia: clinging to outdated success stories despite new realities
Unchecked, these behaviours create echo chambers at the top—where truth becomes optional and risk grows silently.
What Effective Leaders Do Differently
Recognising bias is not enough. Leaders must actively design teams, processes, and systems that invite facts, encourage challenge, and reward intellectual honesty.
1. Normalise Cognitive Dissonance: Encourage teams to see discomfort as a sign of growth. When people feel safe admitting uncertainty, they become more curious and less defensive.
2. Use Structured Dissent: Assign formal roles such as devil’s advocate or run pre-mortem sessions. These mechanisms depersonalise dissent and legitimise critical thinking.
3. Separate Identity from Ideas: Promote the idea that changing one’s mind is a strength, not a weakness. Leaders who model this set the tone for open, adaptive thinking.
4. Slow Down the ‘Snap Yes’: Add cognitive speed bumps to big decisions. Ask: What assumptions are we making? What might we be missing? Who gains if we’re wrong?
5. Reward Truth-Seekers: Recognise those who challenge consensus respectfully, raise red flags early, or bring forward uncomfortable insights. These individuals make your business more resilient.
Final Thought: Resilient Leaders Embrace Discomfort
Leaders aren’t just decision-makers—they’re narrative-shapers. They influence not just what organisations do, but what they believe.
When leadership teams sanitise uncomfortable truths in favour of harmony, they trade clarity for comfort. Over time, that comfort becomes dangerous.
The future belongs to leaders who seek challenge over cheerleading, clarity over certainty, and truth over tribalism. Not because it’s easy, but because the cost of denial is too high to ignore.
The best leaders don’t fear facts. They create cultures that welcome them.
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.

by Atiya Sheikh | May 25, 2025 | Board Members, Board Trustees, CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, General Managers, Heads of Divisions, Leadership Development
Resilience Starts at the Top: How Leaders Can Equip Their Businesses for Disruption
In an age of constant flux, where global shocks and rapid change have become the norm, the role of a CEO has evolved. Today’s leaders must move beyond traditional responsibilities and embrace a more dynamic title: Chief Resilience Officer.
Recent research from McKinsey & Company raises a pressing concern—84% of business leaders say they feel ill-equipped to handle future disruptions, and 60% of board members believe their organisations lack the preparation to face the next major crisis. Yet, amid this uncertainty, leaders can adopt clear, actionable strategies to build resilience and position their organisations for sustainable growth.
Understanding the Five Dimensions of Resilience
To lead effectively through disruption, CEOs must recognise that resilience spans multiple dimensions. McKinsey outlines four key areas:
-
Financial Resilience – The flexibility, liquidity, and access to capital organisations need to weather setbacks and seize opportunities.
-
Operational Resilience – The agility to pivot business practices swiftly and at scale.
-
Organisational Resilience – The cultural and structural strength that enables teams to adapt and recover from setbacks.
-
External Resilience – The strength of stakeholder relationships—including clients, regulators, and investors—that stabilise and support the business.
At inemmo, we believe organisations must also prioritise a fifth dimension:
-
Digital Resilience – The ability to adapt, protect, and thrive in an increasingly digital world. This includes countering cyber threats, embracing emerging technologies, sustaining operations through digital platforms, and enhancing digital capabilities across all levels of staff.
In our global leadership work, we regularly observe how digital fragility can undermine even the most robust strategies. Digital resilience is no longer just part of operational readiness—it has become a strategic imperative.
Embedding Resilience into Organisational Vision
High-performing companies often outperform their peers because their leadership teams align under a shared, resilient vision. CEOs must set this ‘North Star’—a guiding purpose that remains steady in turbulent times.
However, many organisations fail to communicate their vision consistently during uncertainty. CEOs must take the lead in recalibrating their messaging, ensuring it connects long-term ambition with short-term responsiveness. A resilient vision inspires confidence and unifies teams navigating ambiguity.
Linking Resilience Directly to Growth
Resilient businesses don’t wait for disruption to expose weaknesses—they plan ahead. McKinsey reports that 72% of high-performing CEOs set growth targets that exceed the market average. These leaders recognise that resilience acts not only as a shield but as a catalyst for progress and innovation.
Practical actions include scenario planning, stress testing, and using periods of calm to build future capabilities. When leaders treat resilience as a growth engine, they position their organisations to seize opportunities amid uncertainty.
Investing in People and ‘Full-Body’ Resilience
Organisational strength relies on more than systems—it depends on people. CEOs must build what McKinsey describes as “full-body resilience” by addressing all five dimensions in an integrated way. Strength in one area should support others when pressure builds.
This requires investment in the adaptability and well-being of individuals across the business. Leaders should prioritise hiring and developing people who remain agile, responsive, and solution-focused—even under pressure.
Strengthening Stakeholder Relationships
In a complex, interconnected world, CEOs must show up as visible, vocal, and values-led leaders. While many executives believe in corporate responsibility, few feel that organisations take meaningful action.
Effective leaders build external resilience by cultivating strong relationships with a wide range of stakeholders—suppliers, clients, policymakers, investors, and media. These relationships grow through authenticity, consistent communication, and the courage to lead conversations on critical issues.
Final Thought
At inemmo, we believe resilient leadership goes beyond managing risk—it requires a mindset shift. In moments of upheaval, CEOs who embrace this expanded role, align their people, adapt their strategies, and build external trust will guide their organisations toward long-term value and impact.
Is your leadership team ready to become resilience architects?
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.

by Atiya Sheikh | May 25, 2025 | Board Members, Board Trustees, CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, General Managers, Heads of Divisions
Succession Planning: The Strategic Discipline That Shapes the Future
Leadership succession is not an event—it is a discipline. Done well, it secures continuity, strengthens organisational confidence, and positions businesses to adapt and grow. But handled poorly, it exposes gaps, disrupts momentum, and undermines long-term performance.
At inemmo, we work with boards and executive teams to treat succession planning as a vital thread of strategy. It is not about filling a vacancy; it is about building a pipeline of leaders prepared to guide the business through whatever comes next.
Embed Succession from the Start, Not the Exit
Succession planning should begin the moment a new CEO or senior leader steps into their role—not when they start thinking about stepping down. Organisations that excel in this space treat succession as an ongoing leadership responsibility, not a reactive process.
Embedding succession planning into the rhythm of executive oversight enables early identification of potential successors and helps ensure long-term readiness.. It allows leadership teams to make informed decisions, avoid last-minute scrambles, and ensure the future is always being shaped—not simply awaited.
The Next Leader Should Be Built for What’s Ahead
One of the most common missteps in succession is choosing someone who mirrors the current leader. While continuity has its place, it should not come at the expense of future readiness.
Boards and leadership teams must look beyond what works now because tomorrow’s challenges will be different. What capabilities will be essential as the business evolves? What leadership style will help the organisation respond to new market forces, emerging technologies, or global uncertainties?
Succession planning must be future-facing. It requires a clear, dynamic leadership profile—one that evolves alongside strategy, culture, and external shifts. Psychometric tools, behavioural assessments and executive development insights provide the evidence needed to identify not just high performers, but high-potential leaders prepared for tomorrow’s demands.
A Strong Handover Builds Confidence and Momentum
A leadership transition is not just about who comes next—it’s about how they are supported. Outgoing leaders play a vital role in enabling a smooth handover. When handled with transparency and structure, this transition builds confidence among investors, employees, and stakeholders.
It is essential that the incoming leader is given both backing and breathing space. A well-executed handover includes mentorship without interference, knowledge transfer without micromanagement, and public endorsement without overreach.
The real measure of a leadership legacy is not only in what was achieved—but in how the next chapter is made possible.
Succession Planning as a Leadership Culture
Truly resilient organisations treat succession planning as a core element of their leadership culture. It becomes part of how talent is developed, how strategy is sustained, and how growth is enabled over time.
At inemmo, we help organisations make succession planning part of the leadership dialogue, not a last-minute discussion. We support boards, senior teams and HR leaders to prepare the next generation of executives—not just to take over, but to take the organisation forward.
Succession is not about replacement. It’s about renewal.
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.

by Joy Maitland | May 25, 2025 | Board Trustees, CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, General Managers, Heads of Divisions
Integration or Implosion? Winning the Culture Battle After a Merger
Mergers and acquisitions are often hailed as game-changing strategies to achieve rapid growth, scale innovation, and strengthen market position. But all too frequently, they fail to deliver the anticipated results. The missing link? Human experience.
At inemmo, our work with executive teams across multiple sectors has revealed a recurring truth: even the most financially sound and strategically aligned acquisitions can unravel when the employee integration journey is overlooked. The greatest risk in any merger is not just technological or operational misalignment—it is the disengagement of the very people expected to drive post-deal success.
The Human Cost of Poor Integration
Employees within acquired organisations often describe the experience as disorienting, isolating, and at times, deeply unsettling. These individuals—many of whom bring invaluable innovation, knowledge, and relationships—are too often left feeling voiceless, underutilised, and disconnected. One described the moment of acquisition news as “like a death in the family.” Such emotional fallout is not only widespread—it has lasting business consequences.
Where this disconnect persists, engagement plummets, productivity stalls, and attrition increases—sometimes for years. Alarmingly, even in cases where the acquisition brings together complementary capabilities, a poorly managed culture clash can erode the very value the deal aimed to create.
The Opportunity: Building a Unified, Respectful Culture
Creating a unified culture doesn’t mean enforcing uniformity. It means aligning behaviours, systems, and values in a way that respects the heritage of both organisations while moving forward with clarity. To achieve this, acquirers must place culture integration on equal footing with legal, financial, and operational priorities.
Based on insights from across the M&A landscape and inemmo’s leadership development expertise, five practices stand out:
1. Conduct a Dual-Sided Culture Assessment
Most firms assess the culture of the company they’re acquiring. Far fewer hold up the mirror to their own. This is a strategic misstep.
A meaningful culture assessment must explore both entities—mapping how they make decisions, manage risk, and engage with innovation. These insights enable leadership to anticipate friction points and clarify the path forward. Cultural differences, if left unexamined, can delay innovation, undermine collaboration, and stifle initiative.
2. Create a Clear, Human-Centred Culture Integration Plan
Integration must be more than a timeline—it should be a leadership commitment to clarity, dialogue, and empathy. Leaders must articulate not only what will change, but why. They should equip managers with the rationale, resources, and autonomy to bridge cultural gaps with authenticity.
This is especially true when legacy cultures hold prized traits—entrepreneurial energy, speed, creativity—that risk being stifled. As we’ve seen, when acquiring firms pause to explain their methods, rather than impose them, engagement and trust increase.
3. Map the Employee Journey—Before It Begins
A merger feels abstract until it becomes personal. Will their systems change? Who do they report to? How do they apply for leave?
Mapping the employee journey—across 12 to 24 months—allows organisations to prepare for real-life milestones and manage change compassionately. Whether it’s benefits queries, IT logins, or badge renewals, every interaction either builds or erodes trust.
Just as importantly, clarity must replace ambiguity. If certain decisions are still pending, say so. Transparency—even about uncertainty—is more reassuring than misleading certainty.
4. Empower Middle Managers as Culture Translators
Middle managers are the bridge between strategy and reality. Yet too often, they are brought in late, without the information or tools to lead their teams through change.
Equipping these leaders with decision rights, context, and regular access to senior integration teams transforms them into confident, credible guides. They need to be heard—early, often, and visibly—as they carry the message and pulse of the integration.
5. Stay Agile and Responsive to What Emerges
No matter how detailed the integration plan, new insights will emerge. Perhaps the culture is more risk-averse than anticipated. Perhaps legacy rituals, like Friday pizza gatherings, are core to team morale.
Success lies not in rigid execution, but in responsiveness. Build in review phases. Use pulse surveys. Act swiftly on what matters—however small it may seem. Integration is not a one-time event, but a dynamic process that requires real-time adjustment and human leadership.
Cultural Intelligence in Action
At inemmo, we believe cultural intelligence is a decisive advantage during M&As. Leaders who listen closely, communicate clearly, and integrate respectfully not only preserve value—they unlock it.
A successful merger is not just about combining balance sheets or operational systems. It’s about blending ambitions, aligning behaviours, and creating a shared story that people want to be part of.
The deal may be signed in the boardroom. But its true success is determined in the hearts and minds of employees—day by day, conversation by conversation.

by Joy Maitland | Mar 30, 2025 | CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, News & Articles
The Rosebud Phenomenon explains how past experiences—especially unresolved emotional wounds—fuel our ambition. It reveals the deep connection between personal history, professional success, and the pursuit of true fulfilment.
In today’s high-performance business environment, professionals chase success with unwavering focus. Success is widely seen as the ultimate benchmark. However, behind many top performers lies a deeper, often hidden force. This powerful motivator is rarely discussed in boardrooms or biographies. It’s here that the Rosebud Phenomenon offers a fresh and enlightening perspective.
What Is the Rosebud Phenomenon?
The Rosebud Phenomenon refers to the idea that a formative trauma, loss, or emotional void becomes the nucleus of ambition. These early experiences often drive us to achieve, push harder, and stand out. They can sharpen determination and shape professional identity. Yet, this same force may quietly limit long-term satisfaction.
The concept originates from the film Citizen Kane. In it, “Rosebud”—a childhood sled—symbolises lost innocence and a deep emotional need that was never resolved. Likewise, many professionals carry a silent narrative rooted in personal history. This narrative becomes the engine behind relentless performance.
A Double-Edged Sword
Understanding the Rosebud Phenomenon helps leaders and entrepreneurs look beyond surface-level motivation. On the one hand, it drives innovation, ambition, and resilience. On the other, it can keep individuals trapped in a cycle of never-enough.
Executives often feel caught in this paradox. The urge to prove themselves, to heal old wounds, or to rewrite personal stories can deliver impressive results. However, when the emotional source remains unexamined, the journey can lead to burnout, chronic dissatisfaction, or identity conflict.
For example, a leader who grew up feeling overlooked might build a wildly successful company—only to discover they still feel invisible.
The Link Between Meaning and Purpose
The Rosebud Phenomenon offers a clear lens to distinguish meaning from purpose.
Purpose tends to be external—a goal, a title, a mission. Meaning, however, is personal. It’s the internal story we attach to what we do and why we do it.
When professionals build their purpose on unresolved emotional meaning, the two can drift apart. This misalignment often explains why some high achievers feel empty despite checking every box.
They hit the targets. They gain recognition. But the satisfaction fades quickly—because the emotional need behind the success remains unmet.
Implications for Leadership and Growth
Recognising the Rosebud Phenomenon unlocks a deeper level of leadership. It encourages authenticity, emotional insight, and a more human approach to performance. By exploring this dynamic, leaders can align their ambitions with true well-being—not just metrics.
Here are three reflective questions to explore:
- What early experiences shaped my need to succeed?
- Does my definition of success reflect what truly matters to me?
- Am I chasing goals to fill a void—or to express genuine passion?
These questions help shift focus from achievement alone to a more sustainable and satisfying kind of success.
A Personal Note
Some years ago, I had the opportunity to attend a workshop with Dr Stewart Desson, founder of Lumina Learning. The session centred on Lumina Emotion—a tool designed to help individuals understand, adapt, and manage their emotions effectively, empowering them to think clearly and act with purpose. During one of the exercises, I experienced what I can only describe as my own Rosebud moment. It was deeply emotional, completely unexpected, and, if I’m honest, a little embarrassing—especially as a business psychologist who’s facilitated similar sessions myself. Yet in that moment, something shifted. My understanding of my own drivers turned upside down, and the clarity it brought was profound. That experience didn’t just stay with me—it quietly changed the way I view success, fulfilment, and what truly matters.
Final Thoughts
The Rosebud Phenomenon in business provides a compelling framework for rethinking motivation. It invites professionals to look inward—not just upward. In a culture that often celebrates output over insight, this shift is both timely and necessary.
For leaders who seek excellence and inner peace, understanding this dynamic offers a powerful advantage. True success doesn’t just come from what we achieve—but from understanding why we strive in the first place.
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.

by Atiya Sheikh | Mar 30, 2025 | CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, News & Articles
What a 19th-century war game reveals about strategic thinking, adaptability, and decision-making for today’s senior business leaders.
In 1824, a young Prince Wilhelm of Prussia witnessed a military simulation that would go on to change the fortunes of his army—and perhaps the shape of Europe. Kriegsspiel, a war game designed with maps, wooden battalions, and probability tables, was more than a pastime. It became an engine of innovation. Under Wilhelm’s reign, this simulation helped shape military tactics that brought unexpected success in the Franco-Prussian War. Its continued evolution laid the groundwork for predictive logistics, strategic modelling, and ultimately the birth of modern game theory.
For today’s senior leaders, the lesson is clear: when complexity reigns, the ability to model reality—rather than simply react to it—becomes a defining advantage.
Simulating Complexity
The genius of Kriegsspiel was its ability to condense an overwhelming battlefield into a controlled, analytical environment. Its relevance today lies in its approach to complexity. Senior leaders navigating volatile markets, geopolitical shocks, and AI disruption face similarly intricate challenges. The temptation is to act decisively and instinctively—but modelling, simulation, and structured experimentation are far more effective tools.
The most forward-thinking organisations are already building internal “war rooms” that operate in much the same way. They use scenario planning not simply to forecast risk, but to rehearse resilience. Supply chain breakdowns, cyber threats, and consumer shifts are gamed out with cross-functional teams, enabling adaptive strategies long before crisis strikes.
The Leadership Mindset Shift
But the power of simulation lies not in the models alone—it lies in the mindset it cultivates. Prince Wilhelm didn’t simply mandate the use of Kriegsspiel for entertainment. He institutionalised it as a learning tool, embedding it into the professional development of every officer. In doing so, he transformed a military culture from rigid tradition to experimental agility.
Modern business leadership demands a similar shift. Organisations that treat uncertainty as a problem to eliminate will remain brittle. Those that treat it as a landscape to explore—one where tactics can be tested, recalibrated, and refined—will be better placed to navigate transformation with confidence.
This requires humility as much as ambition. Leaders must be willing to ask: What don’t we know? Where might we be wrong? Which assumptions should we challenge? These questions are uncomfortable, but they’re also the entry point to deeper strategic insight.
Models Are Not the Territory
Still, simulation has its limits. Just as Kriegsspiel compressed the battlefield into a tidy map, modern tools—from spreadsheets to digital twins—are simplifications of reality. Kelly Clancy, in her wide-ranging study of how games shape perception, warns that the map can begin to distort the territory. Overreliance on models can lead leaders to prioritise what is measurable over what is meaningful.
The same caution applies to the way game theory and behavioural economics have entered boardroom thinking. When human behaviour is treated as a matter of incentives alone—as though employees, customers or partners are pure rational actors—organisational strategy risks becoming divorced from lived experience.
The best leaders recognise the utility of these models without being seduced by their elegance. They combine data with judgement, logic with empathy. They understand that metrics are tools, not truths.
Designing for Adaptability
In today’s digital environment, game-like mechanisms are everywhere. Reputation systems, social scoring, and algorithmic feedback loops all shape how value is perceived and decisions are made. Businesses too often absorb these mechanisms passively—optimising for clicks, engagement, or customer “loyalty”—without stepping back to ask whether the game they are playing is the one they ought to win.
Leadership today must be more deliberate in shaping the rules of engagement. This means designing organisations not just for efficiency, but for adaptability. It means rewarding learning, not just output. And it means recognising that agility is not the same as chaos—just as improvisation in jazz is rooted in deep discipline.
What a 19th-century war game can teach us about 21st-century leadership
What can a 19th-century war game teach us about 21st-century leadership? More than we might expect. In an age where strategy must be as fluid as the challenges it seeks to overcome, simulation becomes more than a technique—it becomes a habit of mind.
To lead effectively today is to engage with complexity on its own terms. Not to flatten it, ignore it, or hope it goes away. But to step inside it, play it out, and emerge with clearer thinking and sharper intent.
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.
by Atiya Sheikh | Mar 30, 2025 | CEO, CFO, COO, CIO, News & Articles
What makes teamwork effective—and why it fails? In the workplace, no matter the industry—from healthcare and education to finance and tech—success is rarely the result of individual brilliance alone. It’s teams that deliver the results.
But what separates high-performing teams from those that struggle? Why do some groups work like clockwork while others fall into confusion, miscommunication, and missed deadlines?
Welcome to the psychology of teamwork—a field that uncovers what really goes on beneath the surface of collaboration, and how you can build better teams that consistently deliver.
Why Teamwork Is More Complex Than It Looks
Teamwork may sound like a soft skill, but it’s a sophisticated blend of group dynamics, leadership, communication, and role clarity. Psychology first began exploring teamwork through the lens of group identity: how we define ourselves through the teams we’re part of, and how we behave differently when we’re in a group versus acting alone.
Over time, the field evolved. Researchers now examine how teams form, how they make decisions, what makes them efficient—and what makes them fall apart.
When Teamwork Fails: A Real-World Scenario
Let’s take an example from the retail banking world—though the same principles apply across industries.
A customer services advisor meets with a client applying for a mortgage. The standard process involves the advisor gathering initial details and booking a follow-up with a mortgage adviser, who then conducts affordability checks and submits the formal application.
In this case, the advisor assumes the adviser will confirm all financial documentation. Meanwhile, the adviser—new to the branch—believes those checks have already been handled. A key document is missed, the application is delayed, and the client becomes frustrated.
No one was careless. But a lack of shared understanding and clear communication led to an avoidable error.
The Three Pillars of Effective Teamwork: Collaboration, Coordination, Communication
At the heart of any effective team are three essentials:
- Collaboration
True collaboration isn’t just working side-by-side—it’s aligning on a shared goal and appreciating the value of different perspectives. For instance, in a project team, one member might spot a client risk others overlook due to their specific expertise. Strong collaboration means their voice is heard and considered.
- Coordination
Teams must be clear on roles, responsibilities, and timing. Who’s doing what—and when? Without proper coordination, even simple tasks can fall through the cracks, especially in industries with tightly sequenced workflows like healthcare, finance, or manufacturing.
- Communication
Poor communication is the most common cause of team breakdowns. It’s not just about talking more—it’s about ensuring that information is accurate, timely, and reaches the right people.
Why Every Team Needs a Leader—But Not Always the Same Kind
Leadership style can make or break a team. Broadly speaking, there are two main styles:
- Democratic leadership: values group input, ideal for building trust and motivation.
- Autocratic leadership: makes decisions quickly, useful in high-pressure or time-sensitive settings.
The best leaders adjust their approach based on the team’s needs and the task at hand. Interestingly, research shows that gaining power tends to shift people toward more independent thinking—often reducing their willingness to consult others. This is true for both men and women, though women leaders often maintain a stronger group orientation even as they rise.
What Goes Wrong in Group Decisions? Two Common Pitfalls
- Groupthink
This occurs when teams avoid conflict to maintain harmony. Members stop questioning decisions—even bad ones. It’s how warning signs get ignored and poor choices are rubber-stamped. Think of a team launching a flawed product because no one wants to speak up.
- Group Polarisation
Sometimes, groups make more extreme decisions than individuals would. A cautious team becomes overly conservative, or a confident team takes bigger risks than any one member would suggest alone. It’s a distortion of reality that comes from collective confidence—and it can backfire.
Size Matters: Why Smaller Teams Often Perform Better
The ideal team size? Around five people.
Once a team grows beyond that, accountability tends to blur. People assume someone else will take responsibility. This leads to social loafing, where effort drops because everyone believes others are picking up the slack.
In large organisations, this problem scales. When something goes wrong, individuals are quick to say, “That wasn’t my area.” The collective “we” dissolves, replaced by a flurry of self-preservation.
The Cultural Side of Teamwork
Teamwork isn’t just psychological—it’s cultural. In Western countries, the individual is often seen as the core unit. In Eastern cultures like Japan or South Korea, the group comes first.
This plays out in how accountability is assigned. In Europe or the US, a failed initiative may be traced to a single manager. In Japanese firms, the entire team may take collective responsibility.
Understanding these cultural differences is vital, especially for global teams.
How to Build a High-Performing Team
Strong teams don’t come together by chance—they’re built deliberately. Here’s how:
- Keep teams as small as possible for the task
- Define clear roles and responsibilities
- Select members for both technical ability and interpersonal skills
- Create psychological safety where people feel safe speaking up
- Encourage empathy and perspective-taking
In some industries, exercises that ask team members to “step into each other’s shoes” have shown real value. For example, asking a team leader to write from the perspective of a frontline employee can open up new insights into how decisions are experienced on the ground.
Diversity Isn’t Just a Buzzword—It’s a Necessity
Teams that are too similar in mindset, background, or personality often suffer from groupthink. In sectors like consulting or investment banking, hiring from the same profile pool can reduce the range of ideas and increase competition within teams.
The strongest teams are diverse in thought, experience, and working styles—and know how to leverage that difference rather than suppress it.
Final Thoughts: The Future of Work Is Team-Based
Whether you’re delivering financial services, leading a healthcare team, managing a creative agency, or running a non-profit, your results depend on how well your team works together.
The psychology of teamwork offers more than theory—it gives us a framework to build better collaboration, avoid common pitfalls, and unlock real performance.
What makes teamwork effective—and why it fails? Because in the end, success isn’t just about having great people.
It’s about building great teams.
The Right Conversation Can Change Everything. Let’s Talk.
See Harvards Business Review










